Sometimes data frames or a wide range of columns might contain values that you want to remove or replace. Here is how to replace values in the entire R data frame or range of columns.
For example, here is a part of the iris dataset. Let’s imagine that missing values are as a dash symbol.
df <- head(iris) df$Species <- as.character(df$Species) df[3:4, 3:5] <- "-" df # Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species #1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa #2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa #3 4.7 3.2 - - - #4 4.6 3.1 - - - #5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa #6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa
Dash symbol is not useful, and here is how to replace that with NA or any other value.
Replace values in the R data frame
Here is how to replace values in the R data frame by using base R.
df[df == "-"] <- NA
Here are the results of that.
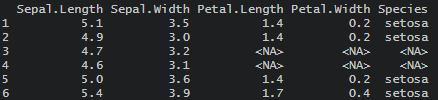
The angled brackets are not the usual way how NA is represented. You can check if there is a difference between <NA> and NA in this case.
As you can see, the function is.na indicates that <NA> is considered as a missing value.
is.na(df) # Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species #1 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE #2 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE #3 FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE #4 FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE #5 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE #6 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
The problem with this approach might be with the numeric columns.
sapply(df, class) #Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species # "numeric" "numeric" "character" "character" "character"
The fastest way how to change to correct data types is by auto-detecting them in R.
df <- readr::type_convert(df) sapply(df, class) #Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species # "numeric" "numeric" "numeric" "numeric" "character"
Replace values in the range of columns in R
Here is how to replace values in the range of columns.
df <- head(iris) df$Species <- as.character(df$Species) df[3:4, 3:5] <- "-" #replace in the range of columns df[, 3:4][df[, 3:4] == "-"] <- NA
The previously mentioned problem with data types remains. In this case, with the numeric columns.
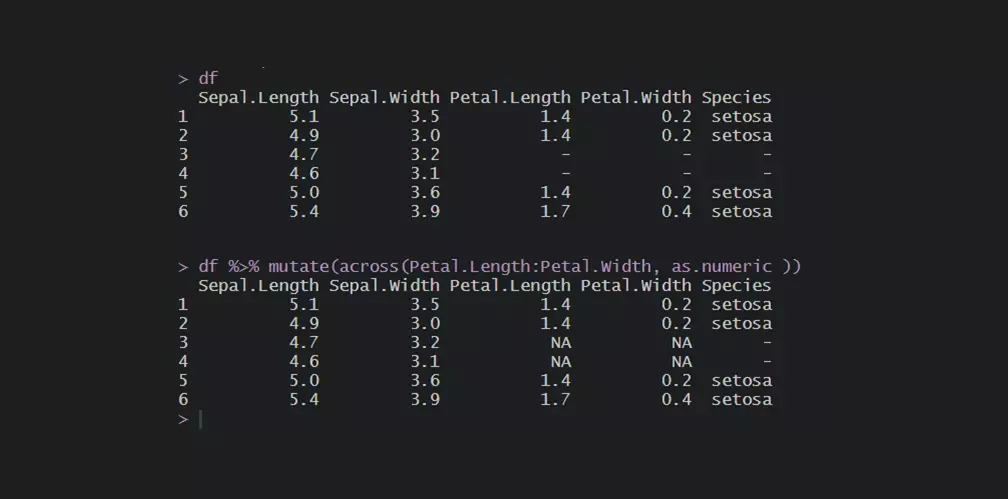
If essentially a numeric column contains a string, you can change the format to numeric, and the NA values will be introduced. The easiest way is to change data types in the range of columns is by using functions from package dplyr.
df <- head(iris) df$Species <- as.character(df$Species) df[3:4, 3:5] <- "-" require(dplyr) #change data type across columns df <- df %>% mutate(across(Petal.Length:Petal.Width, as.numeric)) df # Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species #1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa #2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa #3 4.7 3.2 NA NA - #4 4.6 3.1 NA NA - #5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa #6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa
Here is another post that explains how to deal with unwanted characters in R.
Replace values in R data frame with dplyr
Here is how to do the necessary replacements in the data frame by using dplyr.
require(dplyr) df <- head(iris) df$Species <- as.character(df$Species) df[3:4, 3:5] <- "-" df %>% replace(. == "-", NA)
If you want to replace something specifically with NA, then dplyr contains a function na_if for that.
df %>% na_if("-")Sometimes it is necessary to recode data, and here is a couple of useful examples.
If you like to work with dplyr, then take a look at these tips and tricks.
Leave a Reply